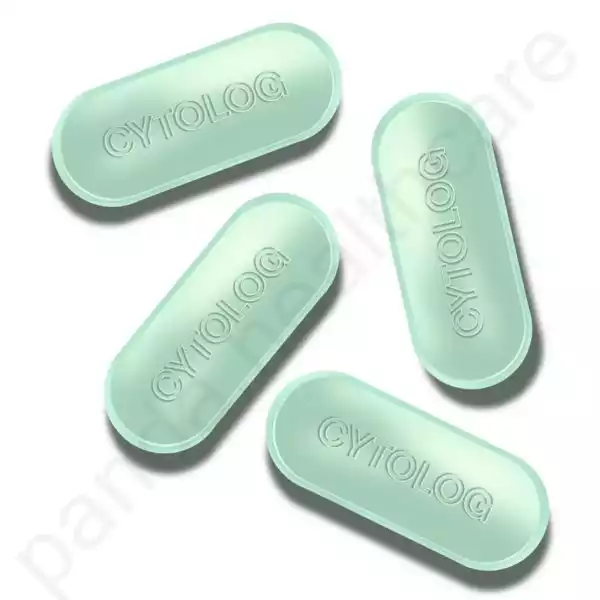
Product description
Cytolog (Misoprostol) — The Complete Product Guide
Introduction:
Cytolog (Misoprostol) is a medication commonly used for various medical purposes. It is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog primarily used to prevent and treat stomach ulcers caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Additionally, Misoprostol is also employed for specific reproductive health issues. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on the uses, dosage, potential side effects, and precautions associated with Misoprostol.
Our online pharmacy has other medications in stock that contain identical doses of Misoprostol: Misoprostol, Misoprost-200, Cytotec, and MisoOne.
Uses:
1. Prevention and treatment of gastric ulcers: Misoprostol prevents stomach ulcers caused by long-term NSAID use.
2. Induction of labor: Misoprostol is sometimes used to induce labor in pregnant women.
3. Medical abortion: Misoprostol, in combination with another medication called Mifepristone (RU-486), can be used for a medical abortion within specific gestational limits established by healthcare professionals.
4. Cervical ripening: Misoprostol softens and prepares the cervix for specific procedures, such as dilatation and curettage (D&C).
Dosage and Administration of Cytolog:
The dosage of Cytolog varies depending on the medical condition being treated. To prevent gastric ulcers, a typical adult dosage is 200 micrograms taken orally four times daily. If Misoprostol is used for labor induction or cervical ripening, a healthcare professional will determine the dosage and administration method.
Side Effects:
Like any medication, Cytolog can cause side effects, although not everyone experiences them. Common side effects may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and headache. These side effects are usually mild and temporary. However, if any side effects persist or worsen, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Precautions:
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Misoprostol should not be used during pregnancy unless specifically prescribed by a healthcare professional. It can cause uterine contractions and may lead to miscarriage or fetal harm. Misoprostol is also not recommended during breastfeeding as it could pass into breast milk.
- Allergies and sensitivities: Individuals with known allergies or hypersensitivity to prostaglandins or other ingredients in Misoprostol should avoid its use.
- Gastrointestinal conditions: Misoprostol should be used cautiously in individuals with a history of inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, or other gastrointestinal conditions.
- Drug interactions: Misoprostol may interact with certain medications, including antacids, magnesium-containing products, and other drugs for ulcer treatment. You must inform your healthcare provider about all medicines you are taking.
Conclusion:
Cytolog is a versatile medication commonly used for gastric ulcer prevention, reproductive health issues, and other medical procedures. It is vital to use Cytolog under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Always consult a healthcare provider to understand the appropriate dosage, potential side effects, and precautions specific to your situation.
 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Русский
Русский

The meeting was pretty productive and was followed by a very welcoming staff from a highly reputable online pharmacy that offers genuine MTP Kits. They handled every aspect of the order process well.